PostgreSQL Backups
Managed Service for PostgreSQL protects the data that you store in your clusters and creates backups for them. The service supports two types of backups:
Automatic backups that Managed Service for PostgreSQL creates daily based on the cluster configuration that you set.
Manual (or on-demand) backups that you create.
Once a backup is created, you can restore a cluster from it.
Backup Details
Here is a sample details page showing the backups that have been performed automatically and manually:
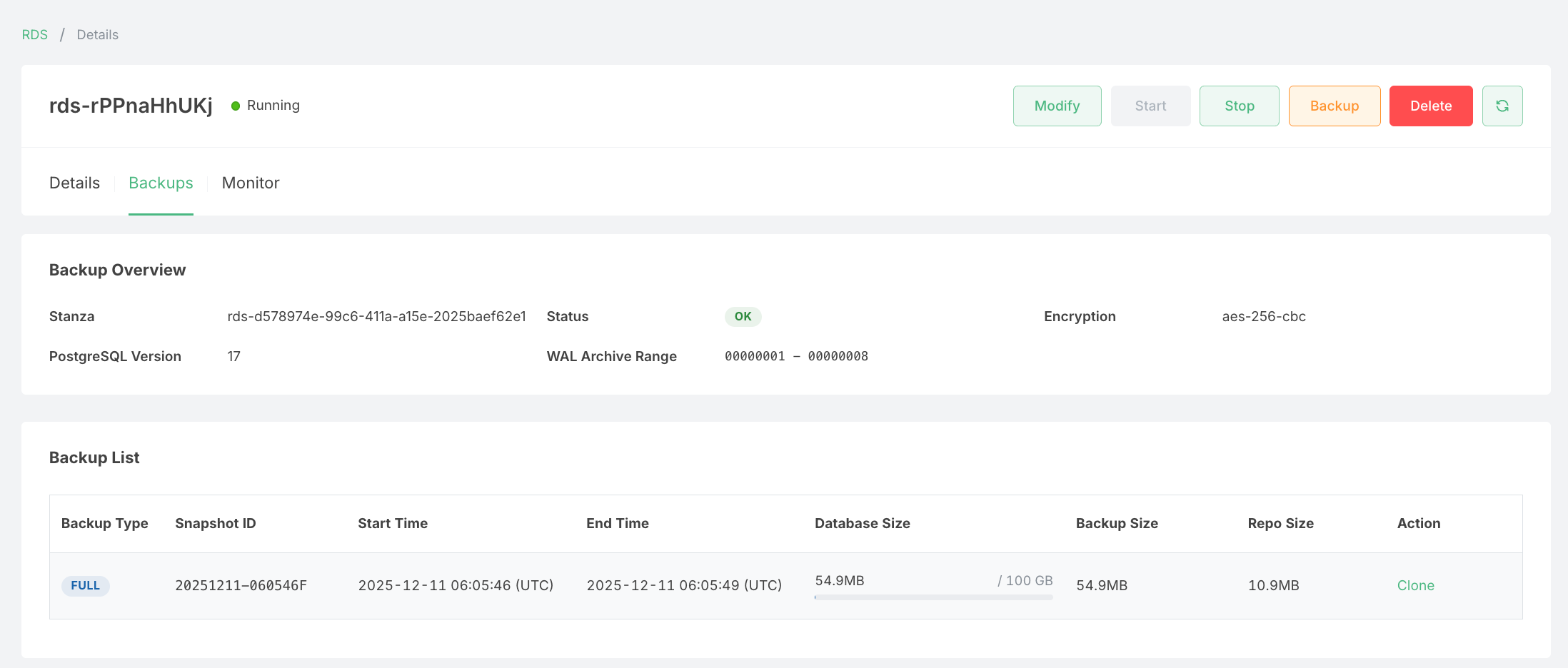
Backup Overview
The Backup Overview section displays key information about your backup configuration:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Stanza | The unique identifier for the backup repository associated with your RDS instance. |
| Status | The current health status of the backup system. A green "OK" indicates backups are functioning normally. |
| Encryption | The encryption algorithm used to secure your backups (e.g., aes-256-cbc). |
| PostgreSQL Version | The version of PostgreSQL running on your RDS instance. |
| WAL Archive Range | The range of Write-Ahead Log (WAL) segments that have been archived, enabling point-in-time recovery. |
Backup List
The Backup List table shows all available backups for your RDS instance:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Backup Type | The type of backup: FULL for complete database backups, or INCR for incremental backups. |
| Snapshot ID | A unique identifier for the backup snapshot, formatted as YYYYMMDD-HHMMSS followed by a type indicator. |
| Start Time | The timestamp (UTC) when the backup process started. |
| End Time | The timestamp (UTC) when the backup process completed. |
| Database Size | The actual size of the database data, along with the allocated storage capacity. |
| Backup Size | The size of the backup before compression. |
| Repo Size | The compressed size of the backup stored in the repository. |
| Action | Available operations for the backup, such as Clone to create a new RDS instance from this backup. |
Creating a Manual Backup
To create an on-demand backup, click the Backup button located in the top-right corner of the RDS details page. Manual backups are useful when you want to capture the current state of your database before performing major changes or updates.
Cloning from a Backup
You can create a new RDS instance from any existing backup by clicking the Clone action in the Backup List. This is useful for:
- Creating development or testing environments from production data
- Recovering data from a specific point in time
- Setting up read replicas or reporting databases
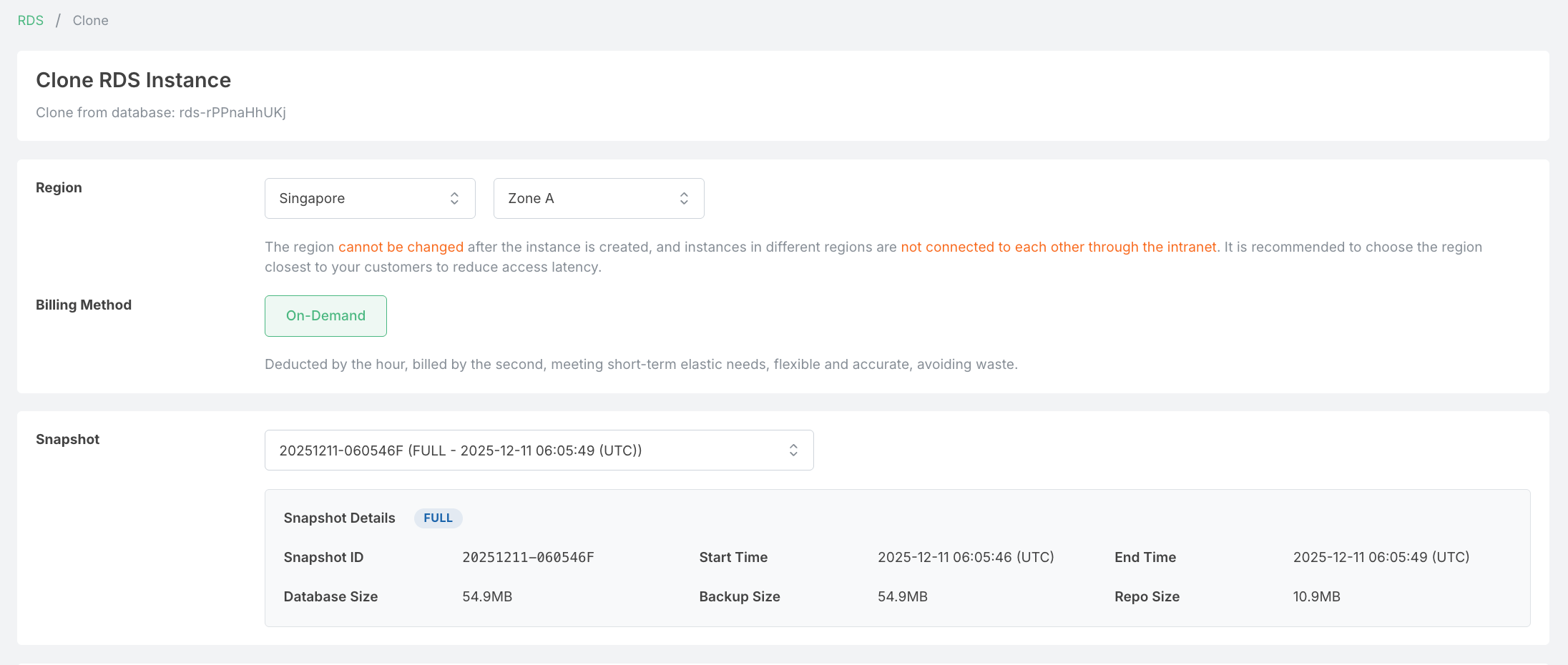
The cloning process follows the same steps as creating a new RDS instance, with the following key differences:
-
Snapshot Selection: You must select a snapshot from the dropdown to restore data from. The snapshot details (ID, start/end time, database size, backup size, and repo size) are displayed for reference.
-
Restricted Fields: The following fields are inherited from the source database and cannot be modified during cloning:
- PostgreSQL Major Version - Must match the source database version
- Database Name - Preserved from the original backup
- Extensions - All installed extensions are carried over from the source
-
Configurable Fields: You can customize other settings such as:
- Region and Zone
- Billing Method
- Instance specifications (CPU, Memory, Storage)
- Network configuration